Introduction
Welcome back! Cryptocurrency is an amazing financial opportunity for investors of every level. but it’s also vital to have strong security measures in place. Crypto users are vulnerable to dangerous online threats. When setting up your investment portfolio or preparing to conduct crypto transactions, you should first get familiar with these threats. We’ve covered security principles for your crypto wallet in past lessons, but there are far more vulnerabilities that need consideration.
This comprehensive lesson will break down multiple common crypto-threats - including those most creative, sophisticated, and insidious. You’ll also learn advanced security measures to prevent and combat these malicious attacks. With these strategies, you’re empowered with the knowledge to keep your crypto holdings and accounts safe.
Understanding Advanced Threats
As cryptocurrency becomes increasingly more popular, crypto-threats also become more sophisticated. Cybercriminals are dedicated to stealing your cryptocurrency; in 2023 alone, around $1.7 billion in crypto was stolen. The vast majority of the theft (95%) occurred through hacking attacks. In 2022, the number was even higher - with $3.8 billion stolen through hacking.
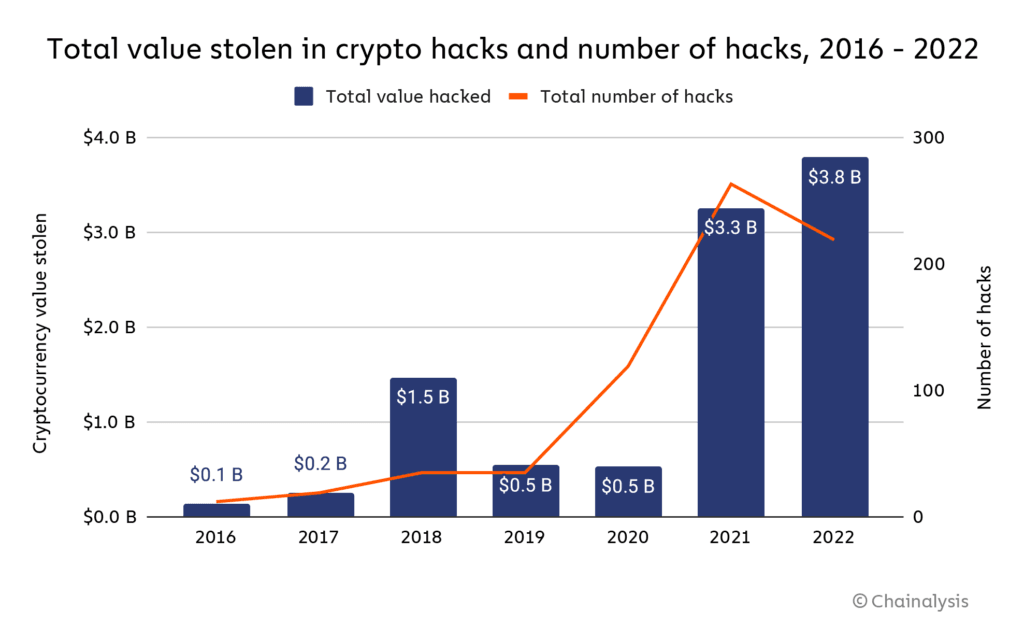
It’s crucial to remain hyper-vigilant of potential security breaches and vulnerabilities. This is especially pertinent due to the nature of crypto. Since crypto transactions aren’t trackable and their systems are decentralized, it’s much harder to recover funds. Cybercriminals search for wallet breaches and system vulnerabilities and even use manipulation to gain access to users’ funds. To combat these attacks, users must adopt a multi-faceted approach.
- Strong Security Measures: Crypto investors can use advanced security measures, such as encryption, two-factor authentication, and security audits.
- Education: Users need to stay up-to-date and aware of common threats, best practices, and recent news.
- Sharing: Often, hackers target multiple users of the same crypto simultaneously. By keeping in touch with your crypto community and sharing experiences, users can ensure they’re staying vigilant and proactive against threats.
The Anatomy of an Attack
To illustrate exactly how hacking and security breaches occur, let’s do a deep-dive analysis of the anatomy of a cryptocurrency attack. While many know of the largest cyberattacks on massive crypto organizations, a security threat for individual traders looks different.
One great example lies in a story shared by Raman Shalupau, a crypto enthusiast and founder of Crypto Jobs List. In 2020, Shalupau set up the brand-new Macbook Pro he had bought one day before. The morning after setting it up, he received a message - someone new had logged into his Telegram account.
Then, he received an email that someone had signed into his Yahoo account and changed the password. Just after that, the hacker signed into his Gmail account and synced their Chrome with it. Minutes later, the hacker got into his Apple account as well. Then, the hacker reached their ultimate goal: Shalupau’s crypto wallets. He watched as the hacker took over $3,000 in ETH, WBTC, UNIs, and other digital assets.
How did this happen and what went wrong?
All this happened within just a few hours! Had Shalupau been away from his devices that morning, he wouldn’t have even been aware of the hacking. So, how exactly did the hacker get his login information? How did they bypass his 2FA?
1. He investigated, quickly realizing that some of his old hot crypto wallets were stored on iCloud.
2. Some of the private keys were saved as password-protected notes in Apple Notes.
3. Some passwords were stored and some as individual files.
It is possible thieves broke into Shalupau’s wallets, using exported passwords from his Google Chrome all while Shalupau’s new Macbook was in hibernate mode.
These hackers went after a specific vulnerability - attacking at the precise moment of Shalupau setting up his new device. Even though Shalupau had 2FA set up for his Apple account, these hackers could still bypass it. The key takeaways? Never store your private crypto information on an online account vulnerable to hacking, and always have 2FA set up - on every account.
Other crypto scams to watch
Pump-and-dumps: This scam is often run by a team of people, who will market a new ‘up-and-coming’ crypto. After promising huge results and generating a buzz, they artificially inflate the crypto’s value to get people to invest. They will then sell at the peak price and abandon the digital currency, causing huge losses to the other investors.
Fake ICOs: Scammers often promote fake initial coin offerings, which is when funds are collected to get a crypto project off the ground. They’ll go so far as to create professional websites, official plans, and even whitepapers to convince investors.
Fake Wallets: Downloading wallet software is common among crypto investors, but scammers can use this as a tool. They can lace actual, otherwise legitimate software with code that redirects your transactions. In the case of you sending or receiving crypto, the funds will instead be sent to the attacker’s wallet.
Building Fortress Defenses

Castles are built with strong defenses to keep the enemy out - moats, huge walls, and lookout towers. Think of your cryptocurrency assets as the treasure inside your castle; fortified with many security measures. You need to keep every part of your castle strong, including your crypto wallet(s), exchange platform account(s), each of your devices, and all related online accounts or platforms. This includes your email, browser, and even social media/messaging accounts.
The first step in building your fortress is becoming familiar with potential threats, which you’re doing now! Once you know what you’re fighting, you can discover how. Here are some of the best practical tips you can implement now to stay safe:
- Independently verify all crypto information you come across. Only follow trusted sources, such as reputable, regulated crypto organizations.
- Use verified software and platforms. Make sure that you are on their official URL, application, or page. Never download software from an unofficial source.
- Enable 2FA (factor authentication) on all accounts.
- Store your information, such as private keys and seed phrases on offline sources (cold storage), or only reputable online platforms with strong security measures.
- Anonymize your transactions. Even though cryptocurrency is already decentralized and not connected to your identity, there are multiple steps you can take to maintain anonymity. One is to mix services - combine your transactions on multiple exchanges and wallets. Another is to use VPNs to keep your IP hidden and secure your internet connection.
Red flags you need to learn
If you spot any of these scenarios, they are red flags and should alert you of a fraudulent situation.
- Unrealistic promises and anonymous teams: Scams often promise huge results and lofty profits with little factual data to back them up. If it seems too good to be true, do a deep dive to figure out why. Many scams aren’t transparent about their team, technology, or processes - ask these questions to find out their legitimacy.
- Pressure to act: If someone is pressuring you to take action quickly, it’s suspicious. Even if your funds were at risk, you would have enough time to research the issue properly and contact support for help.
- Unsolicited offers: Cybercriminals often promote their scams on social media or through websites, and will even reach out to people directly. If you receive unsolicited offers from an unofficial group or individual, stay wary.
- Unregulated organizations: Scams operate on unregulated, unmonitored platforms, or in regions with less government-imposed protections. Real crypto organizations are transparent about what regulatory framework they have in place.
The “Anti-Social Engineer” Tactics
Social engineering is a tactic many cybercriminals use to gain access to your accounts. It describes how hackers use people’s behavior, emotions, and beliefs against them. Let’s deconstruct the most common social engineering scams and the practical methods you can use to avoid them.
Baiting: Baiting attacks take advantage of a person’s greed or curiosity. One very popular example is the promise of wealth - like emails that say you’ve won a free reward. In the crypto world, these scams might say that you are eligible to receive free crypto with a hyperlink or file attached. Once you click on this infected attachment, malware is installed onto your device.
Phishing: Phishing scams often target your fear (or trust). Many phishers pose as a trusted company, such as the crypto trading platform you use. They might send you a message saying that your account is compromised, asking you to reset your password. Once you enter your information into their fake website, they’ll use it to attack your accounts.
Scareware: This scam also exploits fear - usually with a false threat that your account or device is compromised. They will try to get you to install software or click a button to ‘fix’ the issue, claiming there will be dire consequences if you don’t.
Blackmail: This scam exploits a person’s sensitive information. It may include the scammer impersonating someone else to gain compromising photos or other personal data. If the victim doesn’t send funds, they threaten to send these materials to the victim’s family members, employers, and others. Even though this is scary, it’s best to not engage with the blackmailer or send them any crypto. Instead, document all their threats, don’t reply, check the security of all your accounts and personal information, and get the authorities involved.
Pretexting: This attack is especially malicious; establishing some type of trusting relationship to exploit a person’s information. They may pose as a potential employer, advisor, or official, and ask you for personal data to ‘verify’ your identity. Another common pretexting scam is pretending to engage in a romantic relationship with their victim. The scammer will often pretend to be someone else to build a strong connection, then create a false emergency and request your crypto funds.
Stay vigilant (for life)
Staying safe from these security threats is an ongoing journey! Even after setting up your privacy protection measures, it’s crucial to keep vigilant against evolving threats. Research new scamming and hacking techniques, stay updated on others’ experiences, and regularly audit your accounts’ security. To stay sharp, you can routinely assess a comprehensive security checklist to ensure you’re following best practices. The tips we offer above are a great resource, though you can also check out this checklist by Chainsec. Crypto investors should also research the best security and protection tools for their financial strategies; Hacken and Echidna are just two examples!
Course 2.3: Conclusion
The land of cryptocurrency is flush with amazing opportunities for financial profit and tech innovation, but it’s also perilous. When both risk and reward are high, investors have to put security above all else.
Your commitment to protecting your assets and accounts will act as your greatest weapon against cyber criminals. We’ve explored the many types of common scams and security vulnerabilities, even dissecting a real-life example of an attack. Through this guide, we’ve broken down exactly how you can become a vigilant crypto investor, and set up powerful security defenses.




